How to Reduce LLM Cost and Latency in AI Applications
Production AI applications face a critical scaling challenge: GPT-4 costs $10 per million input tokens and $30 per million output tokens, while response times averaging 3-5 seconds create friction in user experiences. For an AI agent handling 10,000 daily conversations with 5,000 tokens per conversation, monthly costs exceed $7,500 on OpenAI alone. When Nielsen Norman Group research shows users abandon applications after 3-second delays, engineering teams must optimize both dimensions simultaneously.
This guide examines how LLM gateways and semantic caching help AI engineering teams reduce costs and improve latency in production applications.
Table of Contents
- Understanding LLM Gateways
- Why LLM Costs Increase in Production
- Why Latency Becomes a Critical Issue
- How LLM Gateways Address Cost and Latency
- Semantic Caching: The Highest Impact Optimization
- Smart Model Routing for Cost Efficiency
- Automatic Failover for Consistent Performance
- Observability and Continuous Optimization
- Implementation Roadmap
- Conclusion
Understanding LLM Gateways
An LLM gateway is a proxy layer that sits between your application and LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, AWS Bedrock, or Google Vertex AI. Instead of your application calling multiple provider APIs directly, it sends requests to a single gateway endpoint that handles routing, caching, failover, and monitoring.
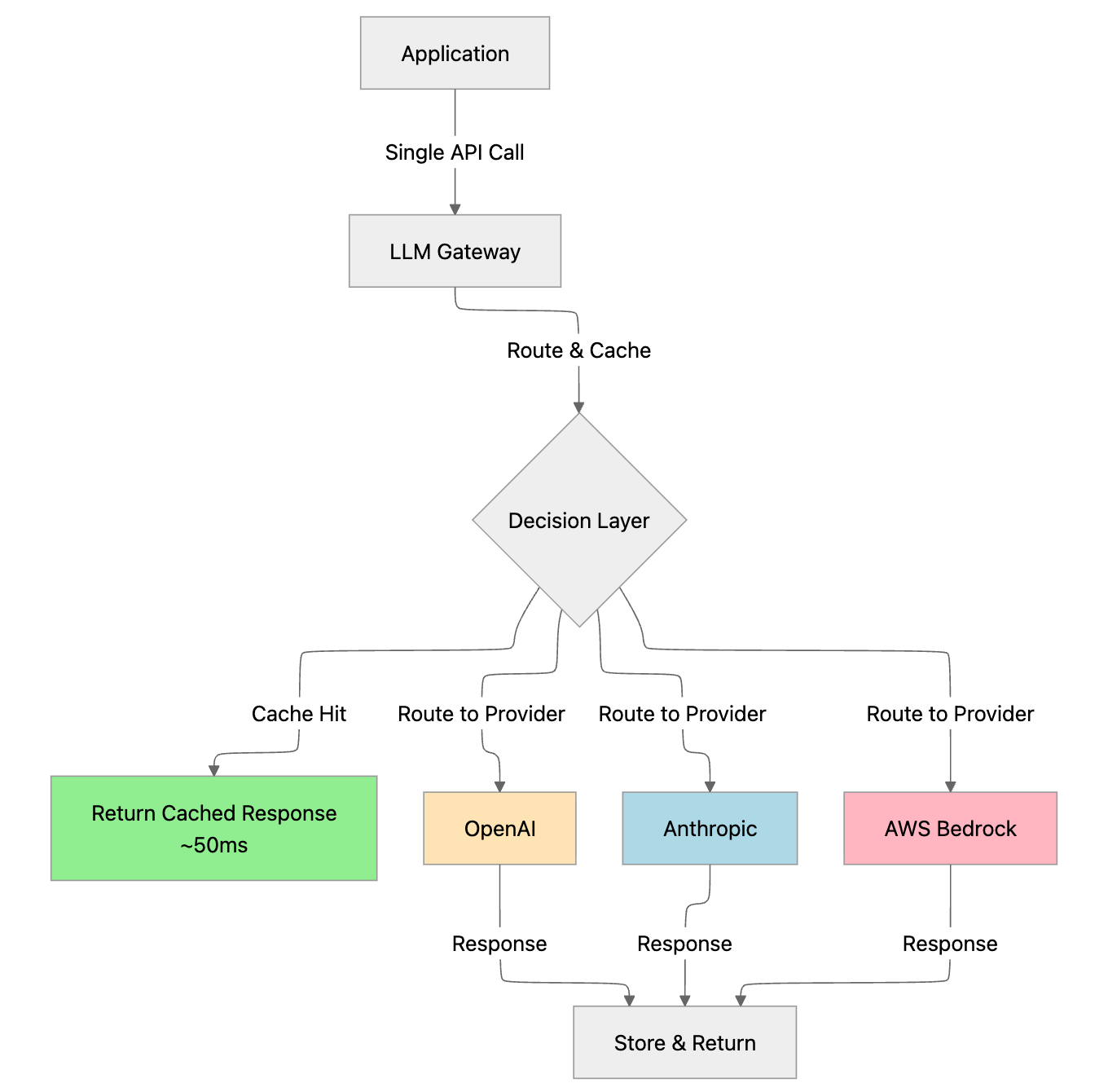
The gateway provides several core capabilities:
- Unified API Interface: Applications use one standardized API format (typically OpenAI-compatible) regardless of which provider actually processes the request
- Request Routing: Intelligent routing logic determines which provider and model should handle each request
- Caching Layer: Stores and retrieves responses to avoid redundant API calls
- Failover Handling: Automatically switches to backup providers when primary endpoints fail
- Cost Tracking: Monitors usage and spending across all providers and models
Bifrost's unified interface demonstrates this architecture by supporting 12+ providers through a single OpenAI-compatible API, enabling teams to switch providers without changing application code.
Why LLM Costs Increase in Production
As AI applications move from prototype to production, several factors cause costs to scale rapidly.
Token Consumption Patterns
Every API call incurs costs based on input and output tokens. Production applications typically include:
- System prompts that provide instructions and context (often 1,000-3,000 tokens)
- RAG context retrieved from vector databases or knowledge bases (2,000-10,000 tokens)
- Conversation history to maintain context across turns (500-5,000 tokens per conversation)
- User input and generated responses (100-2,000 tokens each)
A customer support chatbot with a 2,000-token system prompt, 5,000-token RAG context, and 20-message conversation history easily consumes 15,000+ tokens per interaction. At GPT-4 pricing of $10 per million input tokens, this single conversation costs $0.15 in input tokens alone.
Provider Pricing Variability
Different providers charge different rates for similar capabilities:
- GPT-4: $10 per million input tokens, $30 per million output tokens
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet: $3 per million input tokens, $15 per million output tokens
- GPT-3.5 Turbo: $0.50 per million input tokens, $1.50 per million output tokens
Teams often default to premium models for all tasks, missing opportunities to use more cost-effective models for simpler operations like classification, extraction, or basic question answering.
Redundant API Calls
Production applications frequently process similar or identical requests:
- Customer support chatbots answer "What are your business hours?" hundreds of times daily
- Documentation retrieval systems fetch the same information repeatedly
- Classification pipelines process near-identical inputs
Without caching, each request incurs full API costs even when responses are functionally identical.
Context Window Overhead
Applications that send entire documents or complete conversation histories with every request pay for the same tokens repeatedly. A 30-message conversation that resends full history on each turn processes significantly more tokens than one using intelligent context management. Anthropic's research on context management demonstrates that optimized context handling significantly reduces token consumption without quality degradation.
Why Latency Becomes a Critical Issue
Latency impacts user experience and directly affects application adoption. Nielsen Norman Group research identifies three critical response time thresholds:
- 0.1 seconds: Feels instantaneous
- 1 second: User flow remains uninterrupted
- 10 seconds: Maximum attention span before users disengage
LLM applications face multiple latency sources:
Network Round-Trip Time
Each API call involves network latency between your infrastructure and the provider's servers:
- US-East to provider infrastructure: 80-120ms
- EU to US infrastructure: 150-200ms
- Asia-Pacific to US infrastructure: 200-300ms
These delays occur before any processing begins.
Model Processing Time
OpenAI research shows different models have different processing speeds:
- GPT-4: 3-5 seconds for typical responses
- GPT-3.5: 1.5-2 seconds
- GPT-4o: Under 1 second
Token generation speed varies from 20-50 tokens per second depending on model size and provider infrastructure.
Provider Availability
API providers experience:
- Rate limiting during peak hours
- Capacity constraints during high-demand periods
- Occasional service degradations
When requests fail or timeout after 30-60 seconds, retry logic adds substantial latency to user-facing response times.
Queue Wait Times
During peak usage, providers queue requests based on rate limits and capacity. Applications can experience additional delays on top of processing time, particularly when hitting rate limits.
How LLM Gateways Address Cost and Latency
LLM gateways provide infrastructure that addresses cost and latency challenges through multiple mechanisms operating at different layers of the request lifecycle.
Unified Access to Multiple Providers
By supporting multiple providers through a single API, gateways enable teams to:
- Compare provider pricing and performance
- Route requests to the most cost-effective provider for each task
- Switch providers without changing application code
Bifrost supports OpenAI, Anthropic, AWS Bedrock, Google Vertex, Azure, and more through standardized SDK integrations:
Request-Level Intelligence
Gateways analyze each request to make optimization decisions:
- Cache lookup: Check if a similar request was processed recently
- Model selection: Route to appropriate model based on task complexity
- Provider selection: Choose provider based on cost, latency, or availability
- Failover logic: Switch to backup providers when primary endpoints fail
Response Management
After receiving provider responses, gateways:
- Store responses in cache for future use
- Track token usage and costs
- Log request and response metadata
- Monitor provider performance
Semantic Caching: The Highest Impact Optimization
Semantic caching delivers substantial cost and latency improvements by eliminating redundant API calls while reducing response time from seconds to milliseconds.
How Semantic Caching Works
Traditional exact-match caching only works for identical requests. Semantic caching uses vector embeddings to identify similar requests regardless of wording:
- Generate embeddings: Convert the request into a vector representation using embedding models like OpenAI's text-embedding-3-small
- Compare similarity: Use vector similarity search to find cached entries with high semantic similarity
- Serve cached response: Return the cached response if similarity exceeds the configured threshold (typically 0.8)
Research from Stanford on dense retrieval systems demonstrates that semantic similarity matching using embeddings significantly outperforms exact-match approaches for information retrieval tasks.
Example: When a user asks "What are your business hours?" and later someone asks "When are you open?", semantic caching recognizes these as similar requests and serves the cached response.
Dual-Layer Caching Strategy
Bifrost's semantic caching implementation uses a dual-layer approach:
- Exact hash matching: For identical requests (fastest retrieval)
- Semantic similarity search: For related but differently worded requests
This combination maximizes cache hit rates while maintaining response quality. Research from Meta AI on retrieval-augmented generation demonstrates how embedding-based similarity matching improves response quality while reducing computational overhead.
Implementation with Vector Stores
Semantic caching requires a vector store to perform similarity searches. Bifrost integrates with Weaviate to provide:
- Fast vector similarity searches (sub-millisecond retrieval)
- Scalable storage for cached embeddings and responses
- TTL-based cache expiration
- Per-request cache configuration
Configuration Options
Teams can configure semantic caching behavior:
- Similarity threshold: Control how closely requests must match (typically 0.8-0.95)
- TTL (Time to Live): Set how long responses remain cached
- Cache key isolation: Separate caches per user, session, or application
- Conversation awareness: Exclude caching for long conversations where topic drift increases false positive risk
Streaming Support
Semantic caching supports streaming responses, maintaining the same user experience whether content is served from cache or freshly generated. This enables transparent caching for interactive applications.
Practical Impact
For applications with repetitive query patterns (customer support, documentation retrieval, FAQ systems), semantic caching provides:
- Cost reduction: Cached responses avoid API charges entirely
- Latency improvement: Cache hits return in under 50ms compared to multi-second API calls
- Provider independence: Cached responses maintain availability even during provider outages
Smart Model Routing for Cost Efficiency
Strategic model routing based on task complexity reduces costs while maintaining quality standards.
Task Complexity Analysis
Different tasks require different model capabilities:
Simple tasks (classification, extraction, yes/no questions):
- GPT-3.5 Turbo at $0.50 per million input tokens
- Claude Haiku at $0.25 per million input tokens
Standard tasks (summarization, basic code generation, Q&A):
- GPT-4o at $2.50 per million input tokens
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet at $3 per million input tokens
Complex tasks (reasoning, technical problem-solving, creative writing):
- GPT-4 at $10 per million input tokens
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet at $3 per million input tokens
Routing Configuration
Bifrost's unified interface enables routing logic without application code changes. Teams configure rules based on:
- Prompt length or complexity
- User tier (free, paid, enterprise)
- Task type or endpoint
- Request metadata
Example routing strategy:
- Free-tier users route to GPT-3.5 Turbo
- Paid users route to GPT-4o
- Enterprise users route to Claude 3.5 Sonnet with GPT-4 fallback
Quality Validation
Teams should measure quality per route through evaluation frameworks. Maxim's evaluation platform enables teams to:
- Test model performance across representative scenarios
- Compare output quality between models
- Validate that routing maintains acceptable quality thresholds
Adjust routing rules based on measured performance data rather than assumptions. OpenAI's prompt engineering guide provides best practices for optimizing prompts across different models.
Automatic Failover for Consistent Performance
Provider outages and rate limits create latency spikes that degrade user experience. Automatic failover eliminates these delays by routing to alternative providers when primary endpoints fail.
Failover Mechanisms
Bifrost's fallback system monitors provider health through:
- Success rate tracking
- Response time monitoring
- Error pattern detection
When issues are detected, requests automatically route to configured backup providers within milliseconds. This failover occurs transparently to applications.
Load Balancing
Intelligent load balancing distributes traffic across multiple API keys to:
- Prevent rate limiting
- Optimize throughput
- Balance load across providers
The system tracks usage per key, rotates requests to balance load, and adapts routing based on real-time performance metrics.
Reliability Impact
Automatic failover and load balancing improve application reliability by:
- Maintaining availability during provider outages
- Reducing timeout-related errors
- Eliminating manual intervention during incidents
- Preventing rate limit errors through proactive distribution
Observability and Continuous Optimization
Effective optimization requires visibility into cost drivers, latency patterns, and cache effectiveness.
Metrics and Monitoring
Built-in telemetry provides metrics on:
- Cost per endpoint, model, and provider
- Latency distributions (p50, p95, p99)
- Cache hit rates and effectiveness
- Provider performance and error rates
- Token usage patterns
Optimization Insights
Production observability reveals actionable patterns:
- High-cost endpoints that need optimization
- Cache hit rate variations across different query types
- Latency bottlenecks in specific providers or models
- Token consumption trends over time
Performance Validation
Benchmark testing validates performance under load and identifies bottlenecks before they impact users. Teams can simulate production traffic patterns and measure:
- Request throughput capacity
- Cache performance at scale
- Failover response times
- Provider latency under load

Integration with Maxim
Maxim AI's observability platform provides comprehensive visibility into production AI applications, enabling teams to:
- Track quality metrics beyond cost and latency
- Identify production issues in real-time
- Analyze agent behavior across custom dimensions
- Optimize performance across the entire AI lifecycle
Conclusion
LLM gateways and semantic caching provide systematic approaches to reducing costs and improving latency in production AI applications. By implementing unified provider access, intelligent caching, smart routing, and automatic failover, engineering teams can optimize both dimensions without compromising quality.
Semantic caching delivers immediate impact by eliminating redundant API calls while reducing response times from seconds to milliseconds. Smart model routing optimizes the cost-quality tradeoff by matching task complexity to model capabilities. Automatic failover maintains consistent performance despite provider issues.
Maxim AI provides comprehensive infrastructure for building, testing, and optimizing AI applications throughout the development lifecycle. From prompt engineering and experimentation to agent simulation and evaluation and production observability, Maxim enables teams to ship reliable AI agents faster while maintaining cost efficiency and performance at scale.
Schedule a demo to see how Maxim's evaluation platform and Bifrost gateway infrastructure can help your team reduce LLM costs, improve latency, and deploy production-ready AI applications with confidence.
Learn More from Maxim
For teams building production AI applications, Maxim provides comprehensive resources and tools to optimize cost, latency, and quality throughout the development lifecycle.
Technical Documentation
Gateway Infrastructure:
- Bifrost Quick Start Guide
- Semantic Caching Configuration
- Provider Integration Guide
- Custom Plugin Development
SDK Integrations:
Enterprise Deployment
Security and Compliance:
- In-VPC Deployments: Self-hosted infrastructure for data locality
- Custom Plugins: Organization-specific authentication and compliance
- Governance Features: Budget management and access control
Ready to reduce LLM costs and improve latency in your AI applications? Sign up for Maxim to start testing and optimizing your AI agents, or explore Bifrost documentation to deploy a production-ready LLM gateway.