Top 3 Tools for Monitoring LLM Powered Applications in 2025

The deployment of large language model applications in production environments has created an urgent need for comprehensive monitoring and observability solutions. As organizations scale their AI systems, the ability to track performance metrics, detect quality issues, and maintain reliability has become critical for delivering consistent user experiences. This article examines three leading platforms for LLM monitoring in 2025, evaluating their capabilities, key features, and ideal use cases.
Understanding LLM Monitoring Requirements
Monitoring LLM-powered applications differs fundamentally from traditional application performance monitoring. LLM systems generate dynamic, context-driven outputs where ground truth often does not exist. This requires evaluation frameworks that assess coherence, grounding, and potential harmful content rather than simple accuracy metrics against predetermined answers.
Production LLM applications typically operate within complex multi-agent architectures that include external tool calls, API integrations, and retrieval systems. Effective monitoring must extend beyond tracking a single model to provide visibility across the entire application stack. Teams need real-time insights into latency, token usage, error rates, and cost metrics while simultaneously evaluating output quality through dimensions such as relevance, hallucination detection, and toxicity screening.
According to recent industry analysis, the number of LLM-powered applications is projected to reach 750 million by 2025, driving increased demand for specialized observability platforms. Organizations require monitoring solutions that balance performance optimization, accuracy verification, safety compliance, and cost efficiency across production deployments.
Key Evaluation Criteria for Monitoring Tools
Selecting an appropriate LLM monitoring platform requires careful assessment across multiple dimensions. Organizations should evaluate tools based on their ability to provide comprehensive trace visibility, support for evaluation frameworks, integration capabilities, and scalability for production workloads.
Trace and Span Visibility: Leading platforms offer distributed tracing that captures complete request flows through multi-step LLM applications. This includes detailed logging of prompts, responses, intermediate reasoning steps, tool calls, and API interactions. Granular span-level visibility enables teams to identify performance bottlenecks and debug complex agent workflows.
Evaluation Framework Support: Monitoring tools must provide flexible evaluation capabilities that accommodate both automated and human-in-the-loop assessments. This includes support for custom evaluators, LLM-as-a-judge frameworks, statistical analysis, and deterministic rules. The ability to configure evaluations at session, trace, or span levels offers the granularity required for comprehensive quality assessment.
Integration Ecosystem: Production deployments typically involve multiple LLM providers, frameworks, and development tools. Effective monitoring platforms offer native integrations with popular providers including OpenAI, Anthropic, AWS Bedrock, and Google Vertex AI, alongside support for common frameworks such as LangChain and LlamaIndex. OpenTelemetry compatibility ensures seamless integration with existing observability stacks.
Cost and Performance Optimization: Beyond quality monitoring, platforms should provide detailed token usage analytics, latency tracking, and cost attribution capabilities. This enables teams to identify optimization opportunities, detect inefficiencies such as oversized context windows or unnecessary API calls, and maintain budget control across production deployments.
Top 3 tools for monitoring LLM powered applications
1. Maxim AI
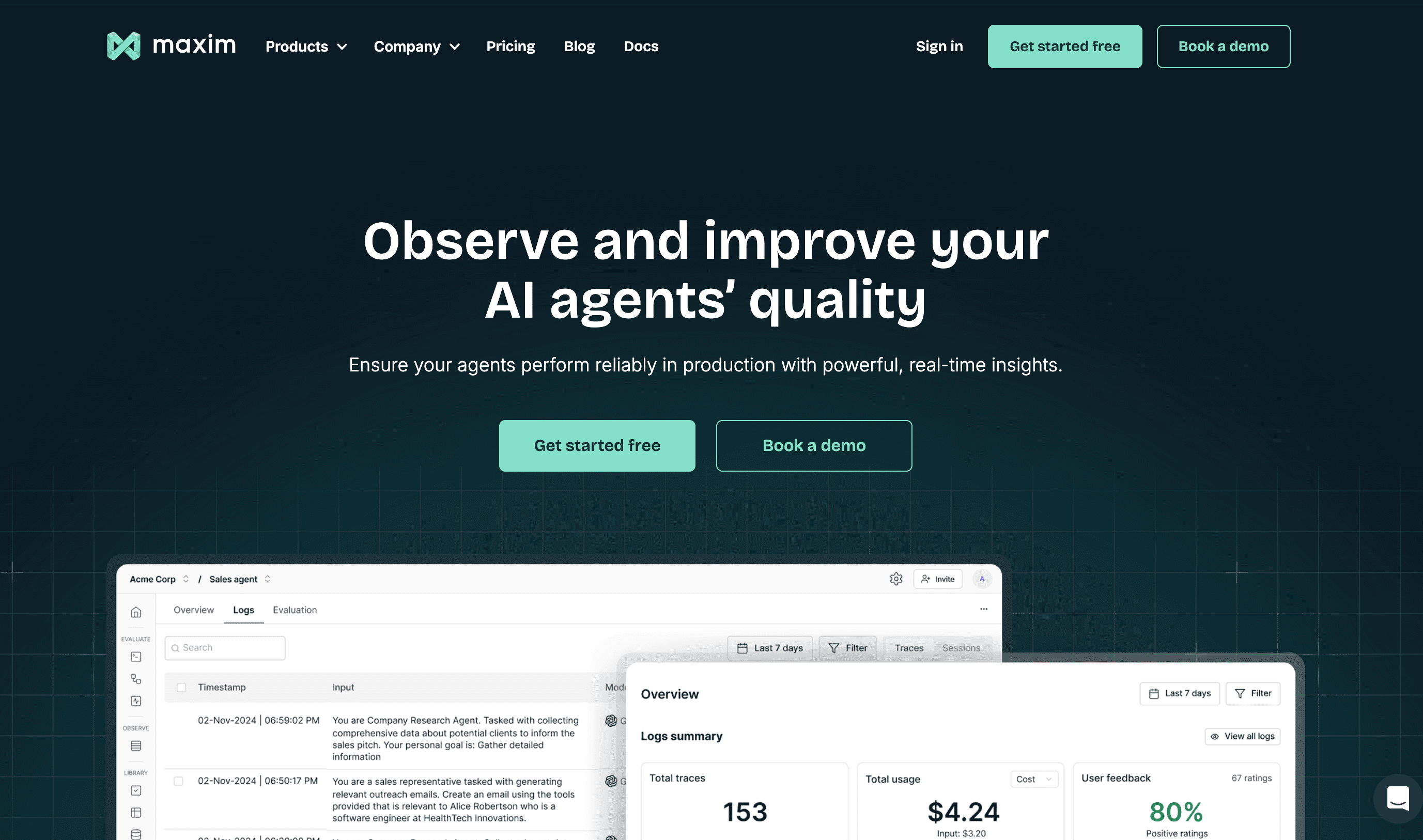
Maxim AI provides an end-to-end platform that extends beyond observability to encompass the entire AI application lifecycle. While observability is a core capability, Maxim differentiates itself through comprehensive support for experimentation, simulation, evaluation, and production monitoring, all designed for cross-functional teams.
Key Differentiators:
- Full-stack lifecycle management: Unlike single-purpose observability tools, Maxim helps teams move faster across pre-release experimentation and production monitoring. You can manage prompts and versions, run simulations against hundreds of scenarios, evaluate agents using off-the-shelf or custom metrics, and monitor live production behavior—all from a unified interface.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Maxim's interface is specifically built for how AI engineering and product teams collaborate. Product managers can define evaluation criteria and run quality assessments without code, while engineers maintain deep control through SDKs available in Python, TypeScript, Java, and Go.
- Distributed tracing with multi-modal support: Maxim provides deep, distributed tracing that captures traditional infrastructure events and LLM-specific elements like prompts, responses, tool use, and context injection. The platform supports text, voice, and vision agents natively.
- Custom dashboards and flexible evaluations: Teams can configure custom dashboards to visualize agent behavior across custom dimensions without dashboard templating constraints. Evaluations are configurable at session, trace, or span granularity.
- Model-centric observability: The platform excels at tracking model versions, comparing their behavior, and identifying degradation patterns.
Core Features:
- Distributed tracing across agent systems with visual timeline inspection
- Automated drift and anomaly detection
- Production debugging and root cause analysis
- Cost tracking and optimization
- Online evaluators that continuously assess real-world agent interactions
- Custom alerting for latency, token usage, evaluation scores, and metadata
- OpenTelemetry compatibility for forwarding traces to Datadog, Grafana, or New Relic
- Prompt management and versioning for experimentation workflows
- Agent simulation for testing across hundreds of scenarios and personas
Best For: Organizations needing comprehensive AI lifecycle management, cross-functional collaboration between engineers and product teams, distributed tracing, node-level evaluations, and multi-modal agent deployments.
2. Langfuse
Langfuse is an open source LLM observability tool, providing tracing, evaluations, prompt management, and metrics to debug and improve LLM applications. The platform has established itself as a choice for teams seeking open source solutions with extensive feature sets and community support.
Langfuse offers comprehensive session tracking capabilities, capturing complete conversation threads and user interactions over time. The platform provides batch export functionality for analysis in external systems, maintains SOC2 compliance and ISO 27001 certification for enterprise security requirements, and includes a prompt playground for interactive experimentation.
The tool integrates seamlessly with multiple frameworks, enabling rapid deployment into existing development workflows. Organizations benefit from the active open source community, which contributes to ongoing feature development and provides extensive documentation for implementation guidance.
3. Arize Phoenix
Phoenix backed by Arize AI is an open source LLM observability platform, designed from the ground up for developers working with complex LLM pipelines and RAG systems. The platform provides specialized capabilities for evaluating, troubleshooting, and optimizing LLM applications through a user interface designed for visualization and experimentation.
The platform visualizes LLM traces and runs during development, enabling teams to understand model behavior before production deployment. Phoenix works well with OpenTelemetry thanks to a set of conventions and plugins that are complimentary to OpenTelemetry, meaning Phoenix can more easily integrate into existing telemetry stacks.
The platform connects to Arize's broader AI development ecosystem, providing observability tools for machine learning and computer vision alongside LLM monitoring. This integration makes Phoenix particularly valuable for organizations working across multiple AI modalities or teams transitioning from traditional ML to generative AI applications.
Conclusion
LLM monitoring has evolved from basic logging to comprehensive observability frameworks that address the unique challenges of generative AI systems. The tools examined in this guide represent different approaches to monitoring, from end-to-end lifecycle platforms to specialized open source solutions, each offering distinct advantages for specific use cases.
Organizations deploying production AI applications should implement monitoring from the earliest development stages, establishing baselines for performance and quality before problems emerge. Effective monitoring enables teams to detect issues early, optimize costs through token usage analysis, maintain quality through automated evaluation, and build trust through transparency into system behavior.
The rapid evolution of LLM capabilities and deployment patterns will continue driving innovation in monitoring tools. Teams should select platforms that provide flexibility for evolving requirements while delivering immediate value for current production needs. Platforms that integrate monitoring with experimentation and evaluation enable faster iteration cycles and more reliable deployments.
Ready to implement comprehensive monitoring for your AI applications? Schedule a demo to see how Maxim can help you ship reliable AI agents faster, or sign up to start monitoring your applications today.


