Top 5 LLM Observability Platforms for 2026

TL;DR
LLM observability has become mission-critical infrastructure for teams shipping AI applications to production. This guide evaluates the top five LLM observability platforms heading into 2026: Maxim AI, Arize AI (Phoenix), LangSmith, Langfuse, and Braintrust. Each platform is assessed across key dimensions including tracing capabilities, evaluation workflows, integrations, enterprise readiness, and cross-functional collaboration. For teams building production-grade AI agents, Maxim AI emerges as the leading end-to-end platform, combining simulation, evaluation, and observability with seamless collaboration between engineering and product teams.
Introduction
The rapid adoption of large language models across industries has fundamentally changed how software teams approach application development. As of 2025, LLMs power everything from customer support agents and conversational banking to autonomous code generation and enterprise search. However, the non-deterministic nature of LLMs introduces unique challenges that traditional monitoring tools simply cannot address.
Unlike conventional software where identical inputs produce identical outputs, LLM applications operate in a probabilistic world. The same prompt can generate different responses, small changes can cascade into major regressions, and what works perfectly in testing can fail spectacularly with real users. This reality makes LLM observability not just a nice-to-have feature but essential infrastructure for any team serious about shipping reliable AI.
The stakes continue to rise as AI applications become more deeply integrated into business-critical workflows. Without robust observability, teams face silent failures, unexplained cost overruns, degraded user experiences, and the inability to diagnose issues when things go wrong. The right observability platform provides the visibility needed to deploy AI systems confidently while maintaining control over behavior as complexity scales.
This comprehensive guide examines the five leading LLM observability platforms positioned to dominate in 2026, analyzing their strengths, limitations, and ideal use cases to help you select the right solution for your organization.
What Makes LLM Observability Different
Before diving into platform comparisons, it is essential to understand why LLM observability differs fundamentally from traditional application monitoring.
The Challenge of Non-Determinism
Traditional software testing relies on deterministic outcomes. You write a test, define expected behavior, and verify the result. LLM applications shatter this paradigm in several ways:
- Variable outputs: The same prompt can generate varied responses even with identical parameters
- Semantic correctness: Output quality often requires qualitative assessment rather than binary pass/fail checks
- Context sensitivity: Performance depends heavily on conversation history, retrieved context, and user intent
- Cascading failures: Issues in one component (retrieval, reasoning, tool calls) propagate unpredictably through multi-step workflows
Core Observability Requirements
Effective LLM observability platforms must address capabilities that traditional APM tools lack:
Distributed Tracing: Capturing complete request lifecycles across prompts, model calls, retrieval operations, tool executions, and agent reasoning chains. This includes visualizing nested spans within complex multi-agent systems.
Evaluation Workflows: Moving beyond simple latency and error metrics to assess semantic quality, factual accuracy, relevance, and task completion rates using automated and human evaluation methods.
Prompt and Response Logging: Recording the full context of interactions including prompts, model outputs, retrieved documents, and intermediate reasoning steps for debugging and analysis.
Cost and Token Attribution: Tracking token usage and associated costs at granular levels to optimize spend and identify inefficient workflows.
Feedback Integration: Capturing user feedback, human annotations, and automated quality scores to continuously improve model performance.
The Top 5 LLM Observability Platforms for 2026
1. Maxim AI
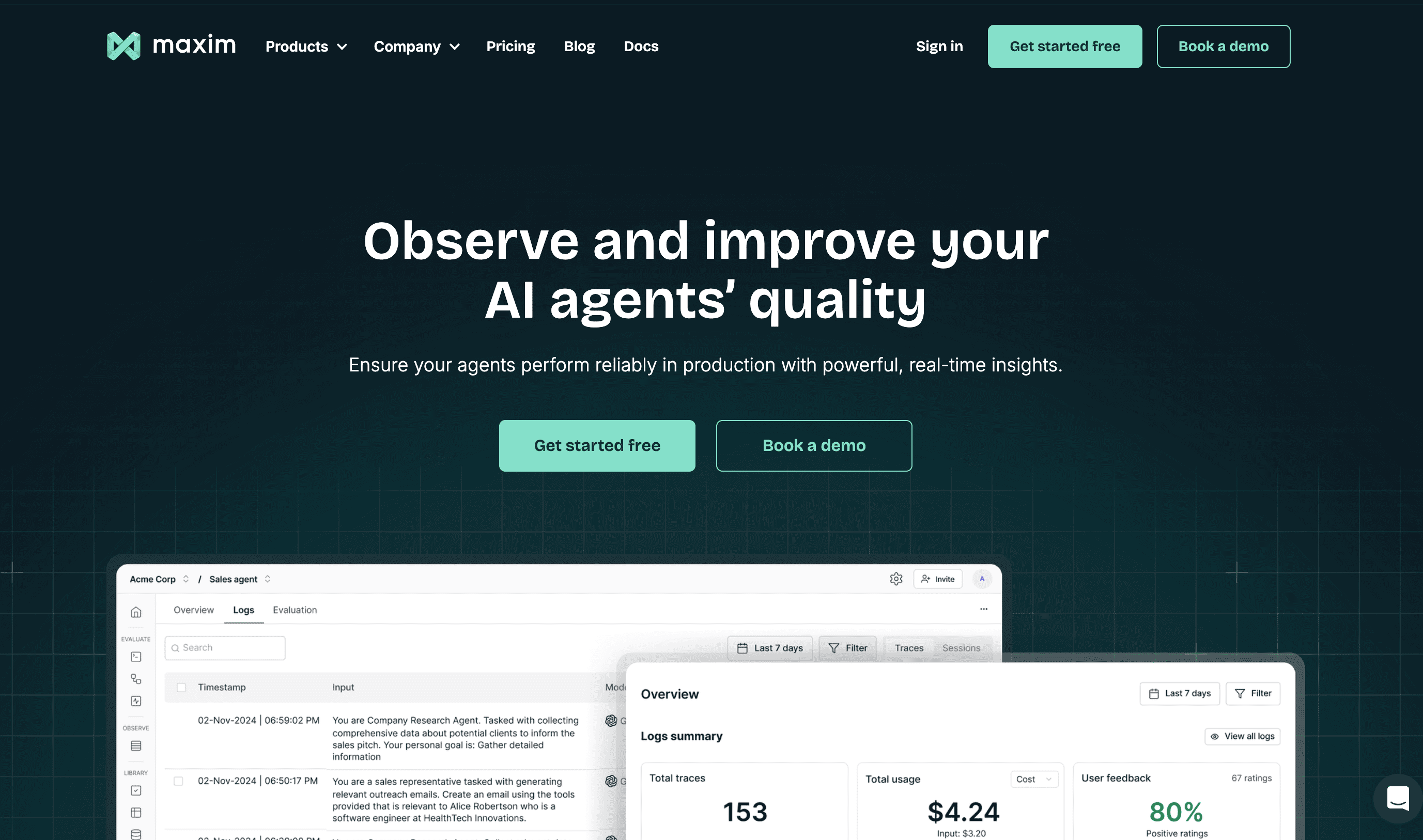
Maxim AI represents the most comprehensive end-to-end platform for AI simulation, evaluation, and observability. Unlike point solutions that address only monitoring or evaluation, Maxim provides a unified framework that covers the entire AI lifecycle from experimentation through production monitoring.
Core Capabilities
Full-Stack Observability: Maxim's observability suite enables teams to monitor real-time production logs and run them through periodic quality checks. The platform supports distributed tracing across sessions, traces, spans, generations, retrievals, and tool calls, providing complete visibility into complex agent workflows.
Agent Simulation and Evaluation: Where Maxim truly differentiates is its simulation capabilities. Teams can simulate customer interactions across real-world scenarios and user personas, evaluate agents at conversational levels, and re-run simulations from any step to reproduce and debug issues.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: The platform is designed for how AI engineering and product teams actually work together. While providing highly performant SDKs in Python, TypeScript, Java, and Go, the entire experience for evaluations can also be driven from the UI without code, reducing engineering dependencies for product teams.
Flexible Evaluation Framework: Maxim offers deep support for custom evaluators including deterministic, statistical, and LLM-as-a-judge approaches, all configurable at session, trace, or span level. The evaluator store provides access to off-the-shelf evaluators while supporting creation of custom evaluators suited to specific application needs.
Enterprise-Grade Data Engine: The platform enables seamless data management including multi-modal dataset curation, continuous evolution of datasets from production data, and data enrichment using in-house or Maxim-managed labeling workflows.
Key Strengths
- End-to-end coverage from experimentation through production monitoring
- Native support for multimodal agents including text, images, and audio
- Intuitive UX enabling product teams to participate in AI quality workflows
- Comprehensive tracing with OpenTelemetry compatibility
- Real-time alerting with integrations for Slack, and PagerDuty
- Custom dashboards for deep insights across agent behavior
Ideal Use Cases
Maxim AI is best suited for teams building production AI agents who need comprehensive lifecycle coverage. Organizations that require cross-functional collaboration between engineering and product teams, those running complex multi-agent systems, and enterprises with strict quality and compliance requirements will find Maxim's full-stack approach particularly valuable.
Companies like Clinc, Thoughtful, and Atomicwork have leveraged Maxim to achieve significant improvements in AI reliability and development velocity.
2. Arize AI (Phoenix)
Arize AI offers a robust LLM observability platform with Phoenix serving as its open-source component. The platform focuses on monitoring, tracing, and debugging model outputs in production environments, with particular strength in traditional ML observability that has been extended to support LLM workloads.
Core Capabilities
Phoenix Open-Source Platform: Phoenix provides an open-source AI observability and evaluation platform built on OpenTelemetry standards. It offers tracing, evaluation, datasets, experiments, a playground for prompt optimization, and prompt management, all available as self-hostable infrastructure.
Comprehensive Framework Support: Phoenix supports major frameworks including LlamaIndex, LangChain, Haystack, DSPy, and smolagents with out-of-the-box auto-instrumentation. This vendor-agnostic approach enables flexibility across different LLM providers.
Evaluation Capabilities: The platform includes an evaluation library with pre-built templates that can be customized, supporting both automated and human annotation workflows. LLM-as-a-judge evaluations enable assessment of accuracy, relevance, toxicity, and response quality.
Enterprise Platform (Arize AX): For larger organizations, Arize AX provides advanced monitoring capabilities including drift detection, bias analysis, and performance monitoring across traditional ML and LLM workloads.
Key Strengths
- Strong open-source foundation with ELv2 license
- Built on OpenTelemetry standards for interoperability
- Deep ML observability roots extending to computer vision and traditional models
- Comprehensive trace visualization and debugging tools
- Native integration with Amazon Bedrock and major cloud providers
Limitations
- Evaluation capabilities feel secondary compared to purpose-built evaluation platforms
- Enterprise features require paid AX platform
- Primary focus remains on observability rather than end-to-end lifecycle coverage
Ideal Use Cases
Arize Phoenix is well-suited for teams with existing ML observability needs who are extending into LLM applications, organizations wanting open-source flexibility with enterprise upgrade paths, and those running complex RAG pipelines who prioritize production monitoring and root cause analysis.
3. LangSmith
LangSmith, developed by the team behind LangChain, offers a dedicated platform for monitoring, debugging, and evaluating LLM applications. As a natural extension of the LangChain ecosystem, it provides seamless integration for teams already using LangChain or LangGraph for application development.
Core Capabilities
Native LangChain Integration: LangSmith integrates directly with LangChain and LangGraph through a simple environment variable configuration. This zero-friction setup means teams can get tracing operational immediately without code modifications.
Comprehensive Tracing: The platform captures complete traces representing end-to-end execution of requests, with each significant operation logged as a run within the trace. Hierarchical visualization makes it straightforward to inspect nested chains, agent workflows, and tool calls.
Production Monitoring: LangSmith provides real-time dashboards tracking LLM-specific statistics including trace counts, feedback scores, time-to-first-token, and performance metrics. The monitoring tab enables viewing trends across different time bins and metadata attributes.
Evaluation Framework: The platform supports systematic testing with datasets, benchmarking against reference answers, and automated evaluation using custom metrics. Integration with human feedback collection enables continuous improvement workflows.
Key Strengths
- Seamless integration with LangChain and LangGraph ecosystems
- Low-friction setup with environment variable configuration
- Strong debugging capabilities with hierarchical trace visualization
- Built-in A/B testing through metadata grouping
- Self-hosting available on enterprise plans
Limitations
- Primary value proposition tied to LangChain ecosystem
- Self-hosting restricted to enterprise tier
- Less comprehensive agent simulation capabilities compared to full-lifecycle platforms
- Product teams may find the interface primarily engineering-focused
Ideal Use Cases
LangSmith is the natural choice for teams heavily invested in the LangChain ecosystem, those building agentic workflows with LangGraph, and organizations wanting the simplest path to observability for LangChain applications. Teams not using LangChain may find other platforms offer better value.
For teams evaluating alternatives, Maxim's comparison with LangSmith provides detailed feature analysis.
4. Langfuse

Langfuse has established itself as a leading open-source LLM engineering platform focused on observability, prompt management, and evaluation. With over 6 million SDK installs per month and strong GitHub engagement, Langfuse has become one of the most popular OSS tools in the LLMOps space.
Core Capabilities
Open-Source Foundation: Langfuse's core is open source under the MIT license, covering essential functionality for LLM observability, tracing, analytics, prompt management, and evaluation. In June 2025, formerly commercial modules including LLM-as-a-judge evaluations, annotation queues, prompt experiments, and the Playground were open-sourced under MIT.
Comprehensive Tracing: The platform captures complete traces of LLM applications including all LLM and non-LLM calls such as retrieval, embedding, and API operations. Support for tracking multi-turn conversations as sessions and user tracking enables end-to-end visibility.
Prompt Management: Langfuse provides tools for managing, versioning, and optimizing prompts throughout the development lifecycle. Strong caching on server and client side enables prompt iteration without adding latency to applications.
Flexible Evaluation: The platform supports LLM-as-a-judge, user feedback collection, manual labeling, and custom evaluation pipelines via APIs and SDKs. Comprehensive APIs enable building bespoke LLMOps workflows using Langfuse building blocks.
Key Strengths
- Fully open-source with MIT license for core features
- Self-hosting flexibility with production-ready deployments
- No LLM proxy requirement, reducing latency and data privacy concerns
- Extensive framework integrations (50+ libraries)
- Strong community support and active development
Limitations
- Enterprise security features require commercial license
- Framework support for newer AI development tools more limited than comprehensive platforms
- Self-hosting requires infrastructure management overhead
- Evaluation runs separate from observability, requiring context switching
Ideal Use Cases
Langfuse is ideal for highly technical teams preferring open-source, self-hosted observability solutions, organizations with strict data residency and compliance requirements, developers wanting maximum control over their observability infrastructure, and startups seeking cost-effective entry points with upgrade paths.
For detailed comparison, see Maxim vs Langfuse.
5. Braintrust
Braintrust positions itself as an AI observability platform for building quality AI products, with particular emphasis on evaluation-first development. The platform integrates evaluation, prompts, and monitoring into a unified experience trusted by companies including Notion, Stripe, and Vercel.
Core Capabilities
Evaluation-First Philosophy: Braintrust treats systematic testing as the foundation upon which everything else builds. Rather than treating evaluations as pass/fail gates, every eval run becomes a full experiment that can be analyzed, compared, and learned from.
Production Monitoring: The platform tracks latency, cost, and custom quality metrics as real traffic flows through applications. Configurable alerts trigger when quality thresholds are crossed or safety rails trip.
Brainstore Database: Purpose-built for searching and analyzing AI interactions at enterprise scale, Brainstore enables teams to ingest and store all application logs with high-performance full-text search across large datasets.
Loop AI Agent: The built-in agent automates writing and optimizing prompts, scorers, and datasets, accelerating iteration cycles for teams scaling their evaluation workflows.
Key Strengths
- Strong evaluation and experimentation capabilities
- High-performance trace search optimized for large datasets
- Native CI/CD integration with GitHub and CircleCI
- Unified platform for text, audio, and multimodal agents
- Innovative in-UI experiences for prompt iteration
Limitations
- LLM proxy approach introduces potential latency and data privacy considerations
- Self-hosting limited to enterprise plans
- Less comprehensive simulation capabilities for agent testing
- Control sits primarily with engineering teams, limiting product team participation
Ideal Use Cases
Braintrust is well-suited for teams prioritizing evaluation and experimentation workflows, organizations needing high-performance search across large trace datasets, and engineering-focused teams who prefer evaluation-first approaches to AI development.
For comprehensive comparison, visit Maxim vs Braintrust.
Platform Comparison Summary
| Capability | Maxim AI | Arize/Phoenix | LangSmith | Langfuse | Braintrust |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tracing | Full distributed tracing with sessions, spans, generations | OpenTelemetry-based tracing | Hierarchical trace visualization | Comprehensive trace capture | Production trace logging |
| Agent Simulation | Native multi-scenario simulation | Limited | Limited | Not available | Limited |
| Evaluation | Flexible evaluators (deterministic, statistical, LLM-as-judge) | Pre-built templates + custom | Dataset benchmarking | LLM-as-judge + custom | Evaluation-first focus |
| Cross-functional UX | Engineering + Product collaboration | Engineering-focused | Engineering-focused | Engineering-focused | Engineering-focused |
| Open Source | No (managed platform) | Phoenix is open source | No (managed + enterprise) | Yes (MIT core) | No (managed + enterprise) |
| Self-Hosting | Enterprise | Yes (Phoenix) | Enterprise only | Yes | Enterprise only |
| Multimodal Support | Text, images, audio | Text, images | Text, images | Text, images | Text, audio |
Key Selection Criteria
When evaluating LLM observability platforms, consider these essential factors:
1. Lifecycle Coverage
Assess whether you need point solutions or end-to-end coverage. While observability may be your immediate requirement, pre-release experimentation, simulation, and evaluation often become critical as AI applications mature. Platforms like Maxim that offer comprehensive lifecycle coverage reduce tool sprawl and enable faster iteration.
2. Team Collaboration Requirements
Consider how engineering and product teams will work together. Platforms with intuitive UIs enabling non-technical team members to participate in AI quality workflows reduce bottlenecks and accelerate development velocity.
3. Integration Ecosystem
Verify compatibility with your existing frameworks, model providers, and infrastructure. Support for standards like OpenTelemetry ensures future flexibility.
4. Evaluation Sophistication
Determine whether basic logging suffices or whether you need sophisticated evaluation capabilities including custom evaluators, human-in-the-loop workflows, and automated quality checks. As AI reliability becomes paramount, robust evaluation frameworks become essential infrastructure.
5. Security and Compliance
For enterprise deployments, verify SOC 2 compliance, data encryption, role-based access controls, and self-hosting options. Consider data residency requirements and whether platforms meet regulatory standards for your industry.
6. Total Cost of Ownership
Look beyond base pricing to understand how costs scale with your application. Some platforms charge based on trace volume or data ingested, which can become expensive at high volumes. Consider whether cost-optimization features offset platform pricing.
Best Practices for LLM Observability Implementation
Regardless of which platform you select, these practices will maximize the value of your observability investment:
Instrument Early: Integrate observability from the start, not as an afterthought. Early instrumentation captures valuable baseline data and establishes good practices.
Standardize Logging Formats: Use OpenAI-compatible message formats for consistency across providers, simplifying debugging and analysis.
Leverage Metadata and Tags: Annotate traces with contextual data including user segments, feature flags, model versions, and environment indicators for powerful filtering and analysis.
Monitor Subjective Metrics: Track user feedback, evaluation scores, and A/B test results alongside objective metrics. Quality evaluation requires both quantitative and qualitative signals.
Automate Quality Checks: Run periodic evaluations using custom rules to maintain production quality and catch regressions before they impact users.
Curate and Evolve Datasets: Continuously refine datasets from production logs for improved training and evaluation. Data quality directly impacts model performance.
Conclusion
The platforms examined in this guide represent the leading solutions heading into 2026, each with distinct strengths suited to different organizational needs.
For teams seeking comprehensive end-to-end coverage that bridges the gap between engineering and product functions, Maxim AI provides the most complete platform for simulation, evaluation, and observability for AI applications. Organizations with existing ML observability needs may find Arize Phoenix offers a natural extension path. Teams deeply invested in LangChain will benefit from LangSmith's native integration, while those prioritizing open-source flexibility should consider Langfuse. Engineering teams focused on evaluation-first workflows may prefer Braintrust's approach.
The right choice depends on your specific requirements for lifecycle coverage, team collaboration, integration needs, and compliance requirements. Whatever platform you select, establishing robust observability practices early will pay dividends as your AI applications scale in complexity and business criticality.
To explore how Maxim AI can accelerate your team's AI development, visit getmaxim.ai or book a demo to see the platform in action.


